Gonorrhoea
Symptoms
About 50% of women and 10% of men don’t experience any symptoms and are unaware that they’re infected.
Women
• Unusual discharge from the vagina
• Pain or burning when weeing
Men
• Unusual discharge from the penis or anus
• Pain or burning when weeing
Gonorrhoea
can be passed
on through:
• Sharing unwashed sex toys
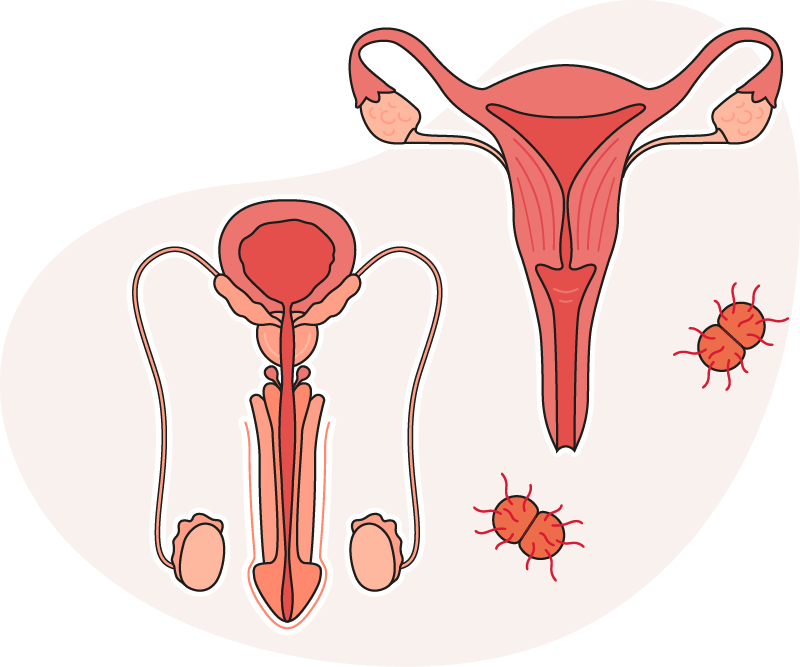
People can develop an infection in the anus, throat or eyes by having unprotected anal or oral sex. If infected sperm or vaginal fluid comes into contact with the eyes, you can develop conjunctivitis.

Getting checked
for Gonorrhoea
There are several ways to check for gonorrhoea. In most cases, a swab test will be carried out (a swab wiped over parts of the body to collect samples of discharge) or you will be asked to provide a urine sample.
You can to talk to your GP, school nurse or pastoral officer if you cannot access the sexual health service or go into a pharmacy for advice.
Treatment
Gonorrhoea is usually treated with a course of antibiotics.
If you are experiencing symptoms, they will usually improve within a few days of receiving treatment.