Chlamydia
It’s particularly common amongst young adults and teens and is passed through unprotected sex.
If you’re sexually active and under the age of 25 in the UK, it’s recommended that you get a chlamydia test once a year, and/or when you have sex with a new partner.
Symptoms
You may experience the things listed below if you do develop symptoms:
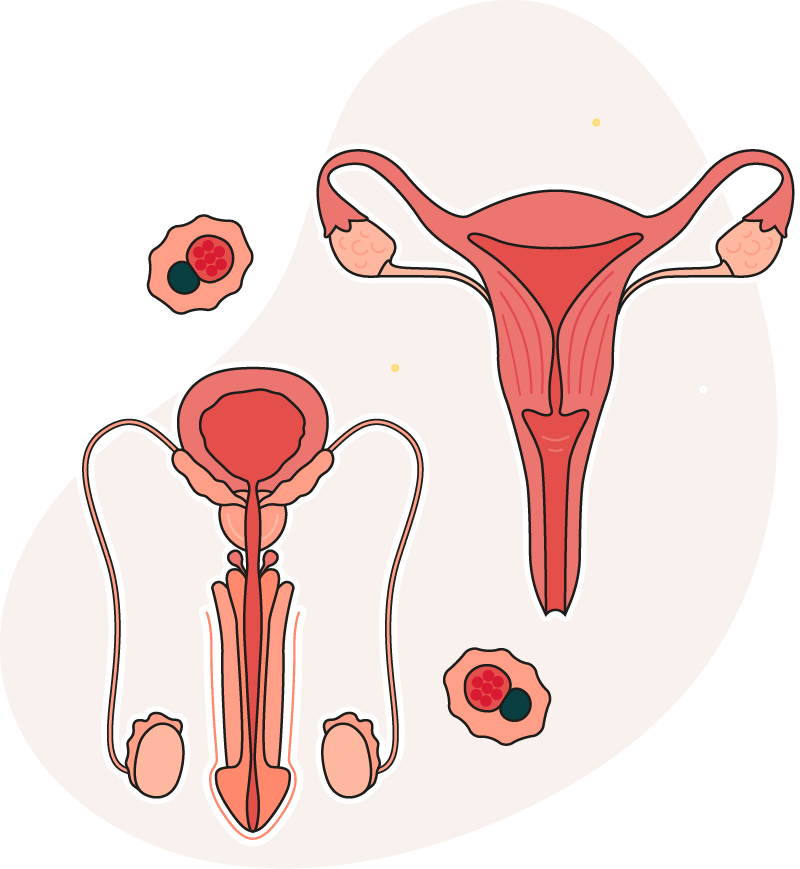
Women
• Unusual discharge from the vagina or anus
• Pain or burning when weeing
Men
• Unusual discharge from the penis or anus
• Pain or burning when weeing
Chlamydia
can be passed
on through:
• Sharing unwashed sex toys
• Infected sperm or vaginal fluid getting into your eye
• Genital contact, meaning you can get chlamydia from your genitals touching another person’s genitals, even if there’s no penetration, orgasm or ejaculation.
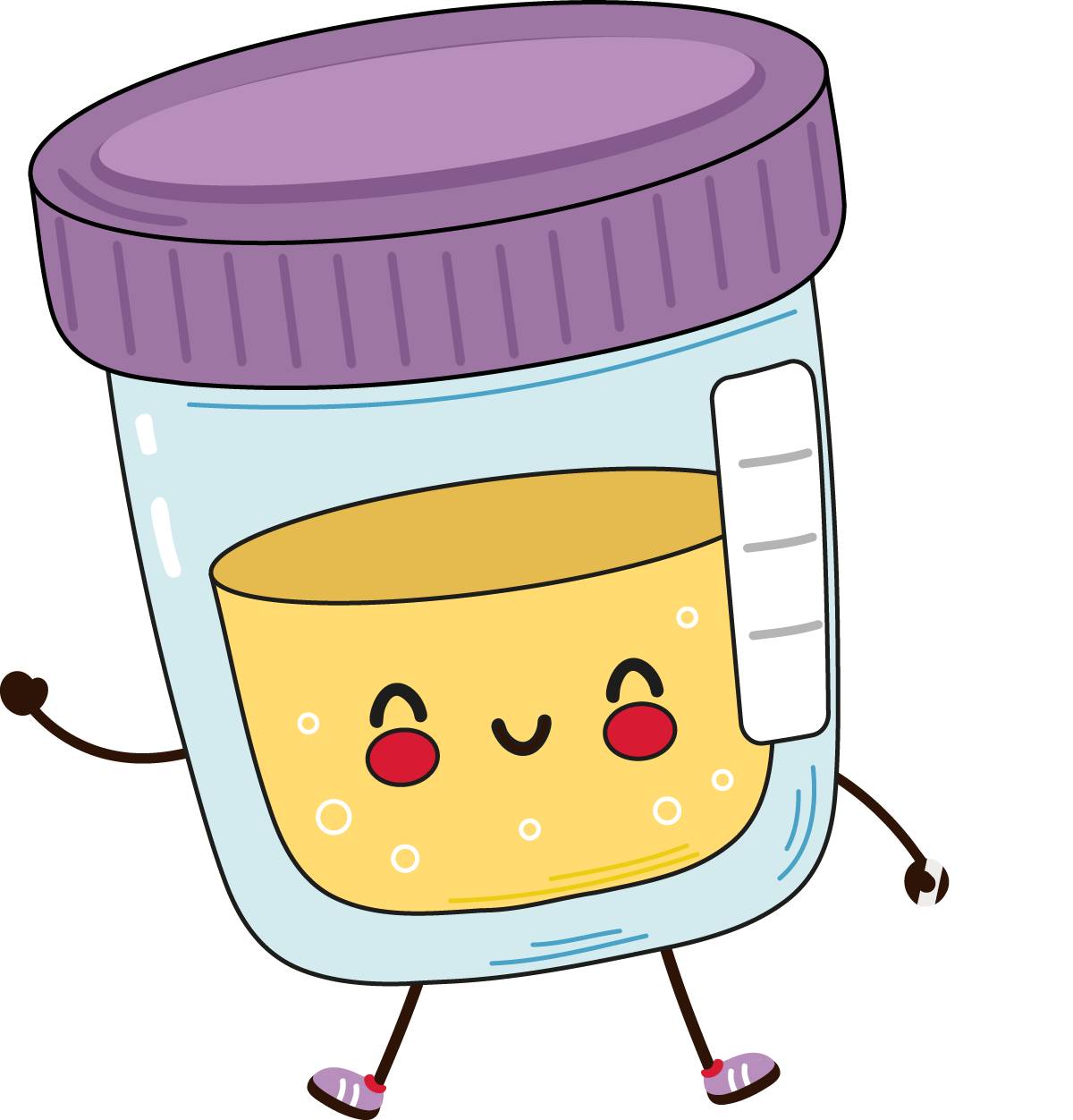


Getting checked for chlamydia
You don’t always need a physical examination by a nurse or doctor.
You can also order a FREE chlamydia testing kit to do at home.
You can to talk to your GP, school nurse or pastoral officer if you cannot access the sexual health service or go into a pharmacy for advice.
Treatment
Chlamydia can usually be treated easily with a short course of antibiotics.
If left untreated, the infection can spread to others parts of the body and lead to long-term health problems.
Untreated chlamydia in men can spread to the testicles and tubes that carry the sperm (epididymis) causing them to become really painful and swollen.
Getting checked and having chlamydia treated as early as possible is important, as the longer it’s left, the higher the chance of more serious complications developing.